Thursday, 26 September 2013
Wednesday, 19 December 2012
6~ Capacitor With a Dielectric
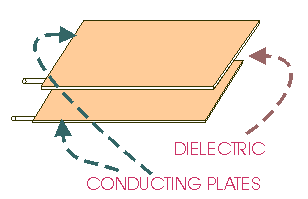

A capacitor
is composed of two conductors separated by
an insulating material called a DIELECTRIC. The dielectric can be paper, plastic film,
ceramic, air or a vacuum.
The plates can be aluminium discs, aluminium foil or a thin film of metal applied to
opposite sides of a solid dielectric.
The CONDUCTOR - DIELECTRIC - CONDUCTOR sandwich
can be rolled into a cylinder or left flat.
Happy Watching !
Do enjoy this video :)
p/s : Do not forget to make your own notes during watching this lesson.
Extra Knowledge !
Capacitance of simple systems
Calculating the capacitance of a system amounts to solving the Laplace equation ∇2φ=0 with a constant potential φ on the surface of the conductors. This is trivial in cases with high symmetry. There is no solution in terms of elementary functions in more complicated cases.
For quasi-two-dimensional situations analytic functions may be used to map different geometries to each other. See also Schwarz-Christoffel mapping.
| Type | Capacitance | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel-plate capacitor |  |
ε: Permittivity
|
| Coaxial cable | 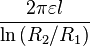 | 
ε: Permittivity
|
| Pair of parallel wires | 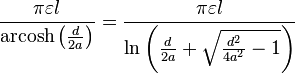 |  |
| Wire parallel to wall |  | a: Wire radius d: Distance, d > a 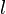 : Wire length : Wire length |
| Two parallel coplanar strips |  | d: Distance w1, w2: Strip width ki: d/(2wi+d) |
| Concentric spheres |  | 
ε: Permittivity
|
| Two spheres, equal radius |    | a: Radius d: Distance, d > 2a D = d/2a γ: Euler's constant |
| Sphere in front of wall |  | a: Radius d: Distance, d > a D = d/a |
| Sphere |  | a: Radius |
| Circular disc |  | a: Radius |
| Thin straight wire, finite length | ![\frac{2\pi \varepsilon l}{\Lambda }\left\{ 1+\frac{1}{\Lambda }\left( 1-\ln 2\right) +\frac{1}{\Lambda ^{2}}\left[ 1+\left( 1-\ln 2\right) ^{2}-\frac{\pi ^{2}}{12}\right] +O\left(\frac{1}{\Lambda ^{3}}\right) \right\}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/8/e/d/8ed16f312307e41ae8adbc3394ac0cdc.png) | a: Wire radius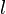 : Length : LengthΛ: ln( 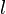 /a) /a) |
Uses of Capacitors
Capacitors are used for several purposes:
- Timing - for example with a 555 timer IC controlling the charging and discharging.
- Smoothing - for example in a power supply.
- Coupling - for example between stages of an audio system and to connect a loudspeaker.
- Filtering - for example in the tone control of an audio system.
- Tuning - for example in a radio system.
- Storing energy - for example in a camera flash circuit.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

